Intro – What is Transformational Leadership? Is it the Best Way to Promote Organizational Change?

Welcome to the world of Transformational Leadership – a guide that unlocks the secrets to leadership that goes beyond the ordinary and inspires positive change. If you’ve ever wondered what makes certain leaders truly exceptional, capable of driving innovation, building strong teams, and getting remarkable things done, you’re in the right place.
In this friendly and insightful guide, we’ll embark on a journey to understand the essence of Transformational Leadership – a leadership style that has shaped some of the greatest successes in history.
From Walt Disney’s imaginative kingdom to Nelson Mandela’s transformative vision, we’ll explore real-world examples that bring the concept to life.
Join us as we delve into the importance of Transformational Leadership, uncover the qualities that make a leader truly transformational, and explore practical steps to incorporate this impactful leadership style into your own professional journey. Get ready to unleash your potential and inspire positive change – let’s embark on this transformative adventure together!
Are you eager to unravel the path ahead? We’ve condensed a brief overview just for you. Prepare to delve into the nuances of transformational leadership, comforted by the assurance that we’re here to accompany you on this enlightening journey.
Quick Summary
Exploring the Dynamics: A Guide to Transformational Leadership
Transformational leadership is a leadership style characterized by individuals who inspire and motivate their teams by setting a positive example. These leaders lead by demonstrating their commitment and values rather than merely instructing others. Transformational leaders possess qualities such as the ability to motivate with a clear vision, earn respect, admiration, and loyalty. An example of a transformational leader is Martin Luther King, Jr., who inspired followers through personal example and encouragement.
In contrast, transactional leadership, exemplified by figures like Steve Jobs, relies more on rewarding positive outcomes and punishing undesired results. While some advocate for transformational leadership as superior, others argue that it has its weaknesses.
This article explores charismatic and transformational leadership, addressing questions about definitions, the four I’s of transformational leadership, traits, notable leaders, strengths and weaknesses, historical context, and the importance of transformational leadership. It also delves into the ongoing debate between transactional and transformational leadership styles, emphasizing that while transformational leadership has been effective in history, its applicability may vary depending on the situation.
Transformational Leadership Through Time: A Historical Exploration
The history of transformational leadership traces back to 1973 when sociologist James V. Downton introduced the term in his book “Rebel Leadership: Commitment and Charisma in the Revolutionary Process.” Downton emphasized the charisma of revolutionary leaders and their ability to instigate change, articulate a vision, and garner loyal followers.
In 1978, James MacGregor Burns expanded on transformational leadership in his book “Leadership,” introducing the Transformational Leadership Theory. Burns distinguished between transactional and transformational leadership, describing the latter as a collaborative process where leaders and followers elevate each other to higher levels of motivation and morality.
Bernard M. Bass further developed the concept in 1985, exploring the psychological behaviors underlying both transactional and transformational leadership. Bass also introduced measurement mechanisms to assess the impact of the transformational leadership model, including the leader’s influence on the team. He defined the four I’s of transformational leadership, contributing to a more detailed understanding of who qualifies as a transformational leader.

Divergent Leadership Styles: Contrasting Transactional and Transformational Approaches
Transactional and transformational leadership, despite appearing as opposing styles, can complement each other, as suggested by Bass’s writings on transformational leadership traits enhancing transactional leadership effectiveness. Both styles have distinct traits:
Transactional Leadership Traits:
- Hierarchy, order, and structure.
- Relies on rewards and punishments for motivation.
- Emphasizes results over individual needs.
- Often involves micromanagement and careful monitoring.
- Employees may feel undervalued or dismissed, with a focus on achieving goals through fear-based motivation.
Transformational Leadership Traits:
- Motivational, team-oriented, and vision-driven.
- Emphasis on building mutual respect with individuals.
- Inspires followers to do their best through earned respect.
- Fosters a sense of nurturing and care for employees.
- Encourages loyalty and motivation based on shared vision and goals.
Differences:
- Transactional leadership relies on a reward/punishment system and emphasizes the end goal, often using fear as a motivator.
- Transformational leadership focuses on earning respect and inspiring individuals to perform at their best through loyalty and motivation.
Transformational leadership has advantages, including nurturing employees, building loyalty, and facilitating buy-in for organizational changes. It creates a sense of being part of a team with a shared vision, enhancing individual and collective performance. However, like any leadership style, transformational leadership has its drawbacks.
The Blueprint of Leadership: Qualities That Define a Transformational Leader
The qualities of a transformational leader include:
- Charismatic:
- Transformational leaders exhibit charisma, fostering loyalty and admiration among their followers.
- Good Communicator:
- They effectively communicate an inspirational vision, gaining support and commitment from their team.
- Empathetic Listener:
- Transformational leaders prioritize empathy and active listening, ensuring team members feel heard, respected, and valued.
- Extravert:
- Being “people persons,” transformational leaders are often extraverts who enjoy connecting with others and fostering a team-oriented environment.
- Openness to Experience:
- They possess openness to new experiences, allowing them to articulate big-picture visions and be emotionally responsive to their team.
- Belief in Everyone’s Value:
- Transformational leaders believe in the value of every individual and lead by example, treating everyone with respect and equality.
- Proactive:
- Proactivity is a key trait, as transformational leaders are not content with the status quo.
- They drive significant change, identify opportunities for improvement, and actively contribute to the progress of organizations, institutions, or societies.
Diversity in Leadership: Navigating the Different Dimensions of Transformational Leadership
The 4 types of transformational leadership, often referred to as the 4 I’s, emphasize different aspects that contribute to the charismatic connection a leader establishes with their team:

- Idealized Influence:
- Transformational leaders lead by example, motivating others through a clear vision.
- This involves creating positive relationships based on trust and respect, serving as a positive role model for the team.
- Inspirational Motivation:
- Unlike transactional leaders who use a reward/punishment system, transformational leaders inspire motivation by presenting a compelling vision and showcasing passion and commitment.
- Followers are naturally motivated to follow due to the strength of the relationships formed with the leader.
- Individualized Consideration:
- Transformational leaders excel at connecting individually with each team member.
- They prioritize listening and genuinely caring about individual development, acting as effective coaches and mentors while inviting and respecting feedback from the team.
- Intellectual Stimulation:
- Transformational leaders stimulate their team intellectually, challenging them to generate innovative solutions.
- While some may view this as a potential weakness, it often leads to creativity, experimentation, and a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
These components of transformational leadership, conceptualized by leadership scholar Bernard M. Bass, emphasize the importance of leading by example, fostering motivation through vision, connecting individually with team members, and promoting intellectual stimulation for innovation and growth.
Leadership Architects: Why Transformational Leaders Are Pivotal in Organizations
Transformational leaders are crucial for various reasons, with a significant impact on driving organizational success:
- Driving Innovation:
- Transformational leaders are catalysts for innovation and evolution within organizations.
- Their visionary approach and ability to create a compelling vision empower employees to innovate, excel, and prioritize the team’s success over individual achievements.
- Building Leaders:
- Transformational leadership is essential for nurturing and developing individuals within the organization.
- Unlike transactional leaders, transformational leaders invest time in understanding and mentoring each team member, contributing to their personal and professional growth. This approach builds a pool of potential leaders within the organization.
- Getting Things Done:
- Transformational leaders leverage loyalty and mutual respect to motivate teams effectively.
- Their ability to inspire commitment to a shared vision makes them adept at leading change management strategies with reduced resistance.
- The determination inherent in the transformational leadership style ensures successful project completion, making them effective drivers of organizational initiatives.
In essence, transformational leaders play a pivotal role in fostering innovation, building a leadership pipeline, and achieving organizational goals through their visionary, people-centric, and determined approach.
Detailed Deep Dive
It’s often noted in employee satisfaction statistics that managers are one of the key factors in a decision to stay with or leave a company. The leadership style of those in a management or supervisory position has a lot to do with the performance and satisfaction of their team.
While there are many different leadership styles, one of the most popular, especially when it comes to change management, is the transformational leadership style.
This style comes from the transformational leadership theory, which lays out 4 components of transformational leadership as well as certain qualities and principles found in this type of leader.

Types of Transformational Leadership
What is Transformational Leadership?
A transformational leader is the type of person that leads by inspiring others. They challenge their team to excel by providing a good example to follow.
It can be said that the transformational leadership model means someone that “walks the walk” and doesn’t just tell people what to do. This type of leader will show them and lead by example.
Other transformational leadership characteristics are the ability to motivate people with a clear vision and earn respect, admiration, and loyalty of those they supervise.
To help give you a better picture, one of the transformational leadership examples would be someone like Martin Luther King, Jr. He inspired others to follow his leadership by presenting an example, building others up, and marching alongside them.
Contrast that with a leader, like Steve Jobs, who was brilliant, but did not build employees up in the same way and took a more transactional leadership approach, rewarding good results and punishing results he didn’t like.
See Also: Understanding the Basics of Change Management Best Practices
Do you have questions about transformational leadership advantages and disadvantages? We’d love to hear from you, click here to contact us.
The Debate Between Transactional and Transformational Leadership
Not all believe that there are no disadvantages to transformational leadership. While some say it’s clearly the better style when comparing transactional leadership and transformational leadership, others point to some distinct weaknesses of transformational leadership.
In this OCM Solution insight article, we are going through everything you need to know about charismatic and transformational leadership. We’ll cover some of the most asked questions about this topic, including:
- What is the transformational leadership definition?
- What are the 4 I’s of transformational leadership?
- What are the popular transformational leadership traits?
- Who is a transformational leader?
- Who are some of the famous transformational leaders in history?
- What are transformational leadership strengths and weaknesses?
- What’s the history of transformational leadership?
- Why is transformational leadership important?
- What’s the difference between transactional and transformational leadership?
History has been filled with awe-inspiring leaders who earned the loyalty and devotion of their followers. Is this the best leadership style for all situations? Where do the strengths of transformational leadership work best?
Read on as we dive into this fascinating topic and pull back the curtains on the debate about the benefits of transformational leadership.
What Does it Mean to Be a Transformational Leader?
We’ll start with the typical transformational leadership definition, which is: “A leadership approach that causes change in individuals and social systems.”
That seems pretty short and doesn’t quite inform what most see as the transformational leadership meaning, which is a bit more detailed.
From the quote above, we can expand a bit and explain that transformational leaders have the ability to cause change in individuals and social systems because of the admiration, loyalty, and respect they earn due to their style of leadership.

You’ll often hear the advantage of transformational leadership discussed when organizations are going through a change. Any type of organizational change can naturally meet with resistance. Those with transformational leadership behaviors can often win people over, transitioning resistance into support.
Some of the transformational leadership skills that make people with this style some of the best change leaders and change champions are:
- They foster a team spirit among those they lead
- They respect those they lead and spend time nurturing their talents
- They will work alongside their team
- They set an excellent example for their team to follow
- They understand the strengths and weaknesses of their team
- They encourage creativity and invite input
- They are able to articulate a strong vision to others
We learn a little more about the transformational leadership style definition from an interview that one of the founding fathers of the principles of transformational leadership, James MacGregor Burns, gave on the topic.
In his interview at the Jepson School of Leadership Studies, he stated that, “Leadership is fellowship and fellowship is leadership.” This speaks directly to the ability of transformational leadership strategies to foster a team spirit and loyalty.
One other distinction he noted was that a transformational leader doesn’t just produce change; they “produce INTENDED change.” That’s where the ability of transformational leadership factors into the ability to create a vision that drives an initiative forward.
History of Transformational Leadership
The importance of transformational leadership and the concept itself has been around since 1973. The concept has been through its own transformation and evolution, which is why you may hear the name Downton, Burns, and Bass transformational leadership all associated with this leadership style.
Each of those three scholars had a part in developing the dimensions of transformational leadership.
The history of transformational leadership follows the following timeline of events.
In 1973, sociologist James V. Downton published the book, Rebel Leadership: Commitment and Charisma in the Revolutionary Process. It’s in this work that he first coined the term “transformational leadership.”
The context of his transformational leadership examples was in the charisma of revolutionary leaders described and their ability to create change, foster a strong vision, and bring loyal followers along with them.
In 1978, historian and leadership studies expert, James MacGregor Burns, took the concept further in his book, Leadership. Since his time in the military during WWII, he was fascinated to learn what makes great leaders and how leaders rise from the ranks.
Burns’ Transformational Leadership Theory
Burns’ expansion of how to be a transformational leader included a description of two types of leadership: Transactional and transformational leadership.
This excerpt from his book adds a bit more to the transformational leadership definition: “Transformational leadership occurs when one or more persons engage with others in such a way that the leaders and followers raise one another to higher levels of motivation and morality.”
This is basically describing the environment of shared vision, mutual respect, and motivation that is a cornerstone of the transformational leadership theory.
By illustrating the difference between transactional and transformational leadership, Burns took the entire concept a large step forward.
In 1985, another leadership scholar, Bernard M. Bass, picked up the baton of, “What is transformational leadership?” and took it even farther with more detail.
Bass transformational leadership writings added information on the psychological behaviors at the foundation of both transactional and transformational leadership. He also described measurement mechanisms by which the impact of the transformational leadership model could be assessed.
How much influence the leader has on the team is one of these measures of the advantages of transformational leadership. The Bass transformational leadership explanation also added factors that exemplify who is a transformational leader.
These factors are known as the four I’s of transformational leadership. We’ll get into these 4 elements of transformational leadership further down in this article.
Don’t Miss: Top Coaching Tool with Defined Plans, Templates and Dashboards
Need more information on questions like “What are the weaknesses of transformational leadership?” or “What are the characteristics of a transformational leader?”. Drop us a message and let us know.
Difference Between Transactional and Transformational Leadership
Since Burns first developed his transformational leadership theory, transactional and transformational leadership have been two sides of a coin when it comes to leadership styles.
While they may sound like completely opposite leadership styles, and in many ways, they are, Bass transformational leadership writings posited that transformational leadership traits could make a transactional leader more effective.
Limitations of transformational leadership would play into the notion that a leader could use both styles as needed. This would mean that both transactional leadership and transformational leadership could be useful to an organization.
Here are some of the main traits of both transactional leadership and transformational leadership:
- Transactional Leadership Traits: Strict, structured, reward, and punishment as motivators, emphasis on results rather than individual.
- Transformational Leadership Traits: Motivational, team-oriented, mutual respect, vision-driven, emphasis on building up the individual.
What’s the difference between transactional and transformational leadership?

Difference Between Transactional and Transformational Leadership
Transactional Leadership
Transactional leadership is based upon hierarchy, order, and structure. This type of leadership style uses rewards and punishments to motivate workers. Often, transactional leaders will be micromanagers, feeling that employees need to be carefully monitored.
Unlike the transformational leadership style, which puts a premium on nurturing employees and inspiring them to do their best, transactional leaders emphasize the end goal and reward those that do as they’re told.
Employees managed by transactional leaders may feel dismissed or not valued as a person. They may also feel like their leader cares more about “the numbers” than they do about them.
Where transformational leadership characteristics get employees to do what’s needed based upon loyalty and motivation to be their best selves, transactional leadership will often use fear as a motivator to get employees to do what’s needed.
Transformational Leadership
The transformational leadership meaning describes a leader that earns respect and inspires others to follow, not because of a reward/punishment system, but because they are inspired by the leader to do their best.
The advantages of transformational leadership include that people are nurtured, feel that they’re respected and cared about, and as a result, will be much more loyal to the charismatic and transformational leadership of their mentor.
Transformational leadership meaning in an organization is that it’s generally easier for this type of leader to get buy-in for a change because of the trust and respect they’ve built up.
Components of transformational leadership can often get people to produce remarkable results because they feel like part of a team that is working toward the same vision, rather than just a cog in a machine.
The benefits of transformational leadership in driving teams forward and bringing out employees’ best selves are apparent, but this leadership style is not without some drawbacks.
We’ll look at the strengths and weaknesses of transformational leadership next.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Transformational Leadership
Even Burns’ Transformational Leadership Theory and the Bass transformational leadership understanding both identified that this leadership style wasn’t the be-all and end-all of leadership.
They both noted that there were transformational leadership strengths and weaknesses. Even with so many advantages to this charismatic and motivational style, there was still plenty of room for criticism of transformational leadership.
It’s important for those wondering how to become a transformational leader to be aware of any downsides of the style. While the benefits may outweigh the challenges of transformational leadership, it’s vital to know that it’s not all a bed of roses. Even the most inspirational leaders can have some weaknesses.
Knowing the advantages and disadvantages of transformational leadership can help all styles of leaders. It allows both transactional leadership and transformational leadership to see what they can do to avoid any pitfalls and perhaps learn from one another.
The premise of both the Bass transformational leadership theory and the Burns transformational leadership theory is that both styles have their plusses and minuses, and that an effective leader can incorporate both transactional and transformational leadership styles.
We’ll go through several advantages and disadvantages of transformational leadership below.
Related: The Best Guide for Transformational Leadership in Nursing Practices
Are you looking answers to questions like “What are the the four types of tools a transformational leader uses to inspire followers?” or “Transformational leadership occurs when blank______.” Whatever your question is, feel free to send us a message.
What are the Advantages of Transformational Leadership?
While the disadvantages of transformational leadership might not be as obvious, the advantages typically are easily spotted, both by corporate leadership and the leader’s employees.
They Make People Feel Valued
Transformational leadership behaviors of nurturing employees make those they lead feel valued and respected. Employees that feel valued are much more likely to stay at a company and be loyal as long as that leader is in place.
They Can Motive People to Go Above and Beyond
Because of the strengths of transformational leadership and their own passion for moving towards a clear vision, they motivate those around them to do the same and go above and beyond. This can mean employees stay late or work over a weekend willingly to meet a specific goal.
Can Both Create and Drive Change
One of the valuable transformational leadership skills for organizations is that this type of leader not only can create better ways of doing things, thus driving change; they are also one of the best change agents.
Because of the respect and loyalty that they’ve garnered, it’s easier for them than for other types of leaders to get their team to be excited and supportive of a change.
They Build Leaders
Within the transformational leadership style definition is that they care about the individuals they’re leading and will take the time to develop leadership skills in those people. Thus, many transformational leaders create other great leaders within the organization.
Promote Openness & Ethics
Two of the dimensions of transformational leadership is the openness with their team and the desire to “do the right thing.” This transparency and strong ethical demeanor rubs off on their team and can be a positive for an organization.
Improve Employee Morale
The nurturing and charismatic style of the types of transformational leadership from these individuals keeps employee morale boosted. People feel that they’re valued and thus look forward to coming to work for this type of leader. High morale reduces employee turnover and increases productivity.
Employees Have Freedom to Invent
The principles of transformational leadership give employees the freedom to invent better ways to do their jobs. This can lead to major improvements in an organization that may have never been realized if employees weren’t given that freedom.
The importance of transformational leadership is apparent when it comes to creating a vibrant organization with a motivated and inspired team. But there are certain limitations to transformational leadership that we’ll explore next.
What are the Disadvantages of Transformational Leadership?
Criticism of transformational leadership often argues that it’s not structured enough and has too much focus on vision rather than the bottom line. Here is the other view to consider when looking at the advantages and disadvantages of transformational leadership.
Bottom Line Can Suffer
One of the weaknesses of transformational leadership is that it focuses more on inspiring and motivating but not enough on the bottom line. If employees fall short of expectations, they may think that it’s okay and just part of their growth, rather than realizing the true detriment to the company.
People Are Loyal to the Leader Not the Company
Criticism of transformational leadership is that they’re fostering loyalty to them, not the company. This can mean a mass exodus of employees that follow their inspirational leader to another company if they happen to leave.
They Can Also Increase Resistance to Change
Just as transformational leadership strategies can drive change forward, if the leader isn’t behind a particular change, they can cause their entire team to resist the change making it harder for change managers to overcome resistance.
Can Take Longer to Get Things Done
One of the transformational leadership factors is to be inclusive and foster a team spirit. This can mean that it takes longer for decisions to be made and things to get done because they feel they have to “bring the team in to brainstorm” and go through everyone’s input before making a decision.
Not Enough Detailed Direction
Limitations of transformational leadership include that the style can be too “big picture” and vision-oriented, leaving employees to fill in the blanks without enough direction. This can lead to project failure because employees are confused about exactly what they need to do.
Can Lead to Interdepartmental Problems
Another of the challenges of transformational leadership is that employees may be treated to perks that other employees may not be. This can lead to conflicts within an organization between different departments because employees of transactional leaders might feel jealous of those working under a person with a transformational leadership style.
What are the Qualities of a Transformational Leader?
Before we get into the principles of transformational leadership and the 4 I’s of transformational leadership, let’s discuss some of the qualities that these types of leaders tend to have.
Many famous transformational leaders seem to have been born with some of these qualities. But that doesn’t mean that those wondering how to be a transformational leader can’t learn some of these traits to adopt this leadership style.
When assessing who is a transformational leader in your organization, many will have similar characteristics that make them stand out. They can also be identified by the team they’ve gathered around them.
Transformational leadership behaviors and transformational leadership strengths and weaknesses will tend to be reflected in their team. While each individual won’t necessarily have the same traits as the transformational leader, the group as a whole often will.
What are the characteristics of a transformational leader?
Charismatic
In the very first writings answering why transformational leadership is important by James V. Downton, charisma was a quality noted of this leadership style. Charisma is present in many transformational leadership examples and is one of the reasons they can foster such loyalty.
Good Communicator
Communicating an inspirational vision that others then adopt as their own is another trait of the transformational leadership style. Good communication skills are needed as well to understand the strengths and weaknesses of their team and foster their respect.
Empathetic Listener
What is transformational leadership at the core? For those who are led by this type of leader, it means they feel heard and respected and given the opportunity to express themselves. In order to mentor individuals into leaders themselves, one of the necessary transformational leadership characteristics is to be an empathetic listener.
Extravert
Another of the transformational leadership characteristics is being an extravert, i.e., “people person.” Extraverts tend to enjoy learning about people and are known to have a need for belonging, which helps them foster that team-oriented environment where everyone feels both motivated and loyal.
Openness to Experience
Another quality that has been linked to the transformational leadership model is an openness to experience. This related to their talent for explaining big-picture visions in a way that captivates their team. This openness is also connected to creative expression and being emotionally responsive to others.
Belief That Everyone Has Value
One of the hallmarks of transformational leadership meaning is that they feel everyone has value, and they don’t put themselves above their employees in that regard. They lead by example and don’t ask their team to do anything they won’t do themselves.
Proactive
Charismatic and transformational leadership tends to be the type that drives organizations forward. They don’t just stick with the status quo. Famous transformational leaders are often well known because they’ve been drivers of significant change, being proactive in identifying and creating improvements in organizations, institutions, and societies.
Popular Article: Best Guide for Improving Healthcare Leadership in Healthcare & Social Care
Are you looking for more information on questions like: “What are the main advantages and disadvantages of transformational leadership?” or “How do you define the 3 weaknesses of transformational leadership?” Send a message to our change management team.
What are the Principles of Transformational Leadership?
When researching the principles of transformational leadership, you’ll find references to two different sets of 7 principles.
One set goes back as early as 2001 and was put together by pastor Erik Rees. These are the ones we’ll be discussing as important components of transformational leadership. The other 7 principles of transformational leadership are from author Hugh Blane from his 2017 book.
The article by Erik Rees titled “Seven Principles of Transformational Leadership – Creating a Synergy of Energy” discusses several benefits of transformational leadership. These 7 principles also provide more insight into the different dimensions of transformational leadership.
1. The Principle of Simplification
One of the strengths of transformational leadership is the ability to explain even complicated concepts in one simple unifying statement. The ability to capture a need for change in a vision is one of the transformational leadership skills that allows this leadership style to gather a coalition behind them.
2. The Principle of Motivation
Beyond creating the vision, these types of leaders have the ability to capture the hearts and minds of their followers and motivate them behind the vision and get their commitment to the cause.
3. The Principle of Facilitation
Within the transformational leadership style definition is the ability to help others succeed and evolve. This includes the ability to facilitate learning in both individuals and teams.
4. The Principle of Innovation
This type of leader has the ability to find where change is needed, and proactively initiate and drive a project forward. This principle shows the importance of transformational leadership when it comes to optimizing organizational efficiency and processes.
5. The Principle of Mobilization
Transformational leadership strategies include the ability to enlist, equip, and empower their team to fulfill the vision they’ve laid out. The trust they build with their team and feelings of mutual respect make it easier for them to mobilize willing supporters of change.
6. The Principle of Preparation
This is one of the principles of transformational leadership that some may argue needs work in some leaders. The principle of preparation is about the ability to continually keep learning about themselves through their interactions with others and evolving to be better.
7. The Principle of Determination
If you want to know how to become a transformational leader, determination is a big part of it. It takes a large amount of stamina to be a driving force and to motivate others. One of the challenges of transformational leadership is keeping the determination to continually move forward, so followers are not let down.
These 7 principles of transformational leadership by Rees show how important this concept is. The transformational leadership theory as a whole continues to evolve as more scholars and leadership experts add their input.
What are the Four Elements of Transformational Leadership?
Next, we go back to Bass transformational leadership theories to find a major concept of this leadership style. This concept is the Four I’s of transformational leadership.
Bass stated that there were 4 elements of transformational leadership that were critical to a leader’s ability to inspire, nurture, and develop leadership skills in others.
Why are these called the 4 I’s of transformational leadership? It’s because each element begins with the letter “I.”
Different types of transformational leadership may highlight one area over another (such as one leader emphasizing community involvement and another continuous innovation). However, one of the transformational leadership factors that is a hallmark of this style is the connection to individual team members.
The 4 components of transformational leadership that Bass came up with represent qualities that need to be in place for anyone asking how to become a transformational leader. These are the qualities needed if they genuinely want to inspire, connect with, and nurture the individuals on their team to reach their full potential.
Overview of the 4 Elements of Transformational Leadership
- Idealized Influence
- Inspirational Motivation
- Individualized Consideration
- Intellectual Stimulation
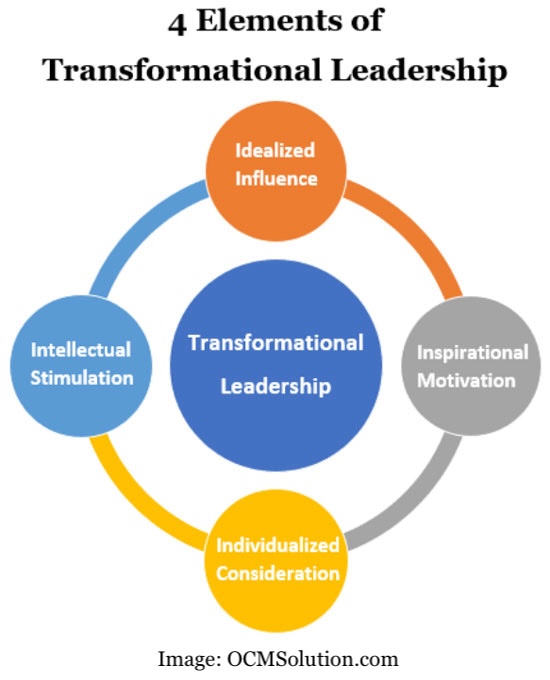
Now, let’s go into each of the 4 I’s of transformational leadership a bit deeper.
What are the 4 Types of Transformational Leadership?
Each of the four I’s of transformational leadership represent different aspects of a leader that allows them to create and keep that charismatic connection with others. The relationship that a transformation leader has with their team is at the heart of this leadership style.
Back when Burns was first exploring transformational leadership examples, he was trying to understand why sometimes those with lower military ranks (like a Corporal) would garner more loyalty and could motive troops better than someone with a higher rank (like a Colonel).
What he found, he described as the difference between transactional and transformational leadership.
As Bass picked up the baton on the transformational leadership definition, he came up with these four I’s of transformational leadership, describing the qualities this type of leader needed to have (i.e., the qualities that that Corporal would have over the higher-ranking Colonel that garnered him more loyalty and respect).
Idealized Influence
How do transformational leaders exert their influence with a group? They have the ability to lead by example and motivate people with a clear vision.
This element in the 4 components of transformational leadership describes the ability to create positive relationships based on trust and respect, which then lead to being able to influence and motivate those they lead.
This boils down to leading by example and being a positive role model.
Inspirational Motivation
If you’ll remember, the transactional leader motivates by a reward/punishment system. Still, the transformational leadership style inspires motivation by creating a compelling vision and through the strength of the relationships they’ve formed with their team.
Followers see the passion and commitment exhibited as transformational leadership characteristics and are naturally motivated to follow.
Individualized Consideration
Another important element of how to be a transformational leader is the ability to connect individually with each person on their team. They listen and truly care about the individual development of team members.
A big part of the answer to, “What is transformational leadership?” is that these leaders are excellent coaches and mentors. They also invite feedback from their team and respect their input.
Intellectual Stimulation
The transformational leadership model is one that stimulates their team mentally and challenges them to come up with innovative solutions. While some may see this as a weakness of transformational leadership because they may see it as too undisciplined and “off the rails,” this quality is often what drives invention and innovation.
This is one of the transformational leadership traits that draws people to want to work under a particular person because they know they’ll be given the freedom to experiment and learn from their mistakes, and they’ll be intellectually stimulated by the team.
Are you looking for more information on questions like: “How can you overcome the transformational leadership advantages and disadvantages?” or “What are the reasons behind the weaknesses of transformational leadership?”Send a message to our change management team.
How Does Transformational Leadership Work?
The transformational leadership style can be learned. Just because you feel you may not have a natural charisma doesn’t mean you don’t have what it takes to adopt transformational leadership characteristics.
What is transformational leadership at its core?
While it’s true some individuals seem naturally disposed towards charismatic and transformational leadership; it’s not really a personality type. It’s a leadership style.
That means that once someone understands the transformational leadership meaning, it’s a style that can be adopted and incorporated into their own style.
How Do You Become a Transformational Leader?
Transformational leadership examples often include leaders that may not have started out being a transformational leader but were able to learn while leading things that garnered the loyalty and respect of their team.
The transformational leadership model works by understanding the key concepts of the style, including the importance of the 4 I’s of transformational leadership.
You can become a transformational leader by studying and incorporating the transformational leadership style into how you coach, lead and motivate your employees or team.
What is transformational leadership? It can include thinking about things a little differently than you do now and being open to change.
Here are a few ways you could incorporate the transformational leadership theory into your own leadership style:
- Take time to get input from your team
- Look for ways to innovate
- Practice simplifying a concept into a 1-2 sentence vision
- Roll up your sleeves and lead by example
- Get to know each person on your team as an individual
- Incorporate mentoring and coaching strategies
- Explore what in your organization you’re passionate about and use that passion to motivate others
- Be bold when it comes to new ideas and trying new things
- Give your team the freedom to try and fail and try again
What is an Example of Transformational Leadership?
Now, let’s take a look at some famous transformational leaders that have made their mark on the world and provide a great illustration of this leadership style.
When wondering, “What is transformational leadership?” the example of these leaders can often tangibly answer that question.
Transformational leadership examples help us understand how there are different types of transformational leadership. Yet, all share the same qualities of leading by example, and the ability to motive and drive their teams forward.
The following are a few transformational leadership examples to illustrate what this style of leadership looks like.
Walt Disney
The famous animator Walt Disney is an excellent example of the transformational leadership style. His vision and storytelling ability not only garnered the admiration of his team but millions of those that love his work.
He also was an innovator, realizing a vision of Disneyland and inventing the idea of what a family theme park could be. To this day, the Disney company carries the transformational leadership definition in its DNA, inviting feedback, challenging people to innovate, and fostering a team spirit.
Nelson Mandela
Nelson Mandela is a great example of the charismatic transformational leadership definition. He was able to bring together cultural divides around his vision of what his country could become.
Mandela is the definition of leading by example. He set forth a bold vision for his people, lived up to it, and expected the same of his followers, who were motivated to follow by his passion.
Mary Kay Ash
One of the other great transformational leader examples is the founder of the Mary Kay cosmetics empire, Mary Kay Ash. Some of the foundational values that she based her company on were treating everyone equally and coaching people to reach their true potential.
This quote by Mary Kay Ash exemplifies one of the core transformational leadership characteristics, “Everyone has an invisible sign hanging from their neck saying, ‘Make me feel important.’ Never forget this message when working with people.”
Martin Luther King, Jr.
The vision of Martin Luther King, Jr. still inspires people to this day. He exemplified the transformational leadership model, inspiring change in civil rights, and building up others along the way.
He served as a role model and worked alongside those he led, fostering mutual respect that garnered loyalty. He set an example that others aspired to follow and is one of the leaders seen as the very transformational leadership definition.
Why are Transformational Leaders So Important?
Why is transformational leadership important? Some of the biggest advances in history may not have happened without the power of the transformational leadership style.

What is Transformational Leadership?
For organizations, the transformational leadership theory is important for several reasons; here are three of the main reasons.
To Drive Innovation
Those with transformational leadership characteristics are always optimizing and evolving. This benefits their organizations because they not only seek out innovation; they can create the vision and drive the change to make it happen.
People fitting the transformational leadership model, create the environments for their employees that cause people to want to innovate, do better, and think of the good of the team over the individual.
To Build Leaders
If a company has too many transactional leaders, ones that don’t take time to build up their team and use a punishment/reward motivation, they may find that their best employees are leaving because they don’t feel nurtured or that they have a path to personal career fulfillment.
What is transformational leadership? It’s leadership that not only transforms an organization or society; it also transforms individuals.
One of the main differences between transactional and transformational leadership is that transformational leaders take time to get to know the individuals they lead and mentor them to grow and evolve these individuals into leaders themselves.
To Get Things Done
Because of the loyalty and mutual respect that those with transformational leadership characteristics build with their teams, they’re able to motivate people to follow a vision. This makes them one of the best leaders of change management strategies because they’ll typically face less resistance than other leaders.
The transformational leadership definition also means that they’re often the ones proactively looking for innovation; therefore, their vision and passion often are the thing that gets things done in large organizations where others may have failed.
There’s a determination in the transformational leadership style that keeps them sticking to a project until it’s completed successfully.
Read More: Best Guide for Transformational Leadership in Education & Schools
Conclusion: Best Guide to Transformational Leadership Theory & Practice
When studying transformational leadership theory and looking at real-life transformational leadership examples, it’s important to remember this. Even though many are born with specific transformational leadership characteristics, like charisma, that doesn’t mean others can’t also become transformational leaders.
Understanding the four I’s of transformational leadership is one way to begin incorporating some of this style’s traits into your own leadership style.
Just as important as learning the advantages of transformational leadership traits is learning the limitations and disadvantages of transformational leadership. Knowing both helps you ensure you’re adopting the best of the style while avoiding any pitfalls.
People don’t necessarily have to choose between transactional leadership and transformational leadership if they fully understand both and can meld the best of the two styles together.
The transformational leadership style is one of the most important for company innovation, change management, and employee retention because of the environment of loyalty, passion, and experimentation it fosters.
It’s also a style that builds leaders that are continually motivated to make themselves and their organizations better.
Note: Content on OCM Solution's ocmsolution.com website is protected by copyright. Should you have any questions or comments regarding this OCM Solution page, please reach out to Ogbe Airiodion (Change Management Lead) or the OCM Solutions Team today. OCM Solution was previously known as Airiodion Global Services (AGS).
Images: https://stock.adobe.com, https://www.pexels.com/photo/group-of-people-having-a-discussion-while-seated-on-the-floor-3863788/, Microsoft 365 Clip Art Image(s) (Bing images licensed under the Creative Commons license system.)