Tools & Models for Stakeholder Analysis (Mendelows, Stakeholder Power Map, Miro & more)
The Best 2024 Tools & Models to Help You with Your Stakeholder Assessment
Change is a constant in any organization, and successfully managing it requires a thorough understanding of the various stakeholders involved. Stakeholder analysis is a crucial aspect of change management that helps identify, assess, and prioritize the interests, expectations, and influence of different individuals or groups.
Using stakeholder analysis models and mapping tools (like a stakeholder heat map) can make the process of stakeholder assessment for a change initiative easier and more effective.
In this article, we will delve into different methods and tools used for stakeholder analysis, shedding light on their unique features and applications. Some of the tools and models we’ll look at include: Mendelow’s stakeholder mapping, stakeholder relationship maps, stakeholder map Miro, a power interest grid, and many more.
What is Stakeholder Analysis?
Stakeholder analysis is a systematic process of identifying, assessing, and understanding the individuals, groups, or entities that can significantly affect or be affected by a particular project, initiative, or change within an organization. These stakeholders, both internal and external, have a vested interest in the success or failure of the endeavor, and their involvement can greatly influence the outcomes.
Stakeholder assessment includes:
- Mapping out the stakeholders according to their level of interest and influence on the change
- Understanding their needs, expectations, concerns and potential resistance
- Developing strategies to communicate, consult and collaborate with them
- Monitoring and evaluating their feedback and satisfaction
Read more: Best Stakeholder Analysis and Mapping Guide for Assessing Stakeholder
Streamline Your Stakeholder Identification and Analysis with OCMS Portal.
Easily create a stakeholder value map and generate an engagement plan based on your assessment. Sign up for a free trial of OCMS Portal today for instant access to this innovative stakeholder analysis tool.
What’s the Purpose of a Stakeholder Analysis?
The purpose of stakeholder analysis is multifaceted. It aims to:
- Identify Stakeholders: The first step is to compile a comprehensive list of all potential stakeholders who may be impacted by the change or project. This includes individuals, groups, or organizations both inside and outside the company.
- Assess Influence and Interest: Once stakeholders are identified, the analysis involves evaluating their level of influence and interest in the project or change. Influence refers to the ability to affect the decision-making process, while interest reflects the extent to which a stakeholder is affected by the outcome. A tool that helps with this is a power interest grid stakeholder analysis.
- Prioritize Stakeholders: Stakeholders are then categorized or prioritized based on their level of influence and interest. This helps in focusing efforts on those who can significantly impact or be impacted by the initiative.
- Understand Expectations and Concerns: The analysis delves into the expectations, needs, and concerns of each stakeholder. This understanding is crucial for tailoring communication strategies, addressing potential issues, and managing expectations throughout the project or change process.
- Develop Strategies for Engagement: A stakeholder power map can inform the development of strategies for engaging and managing relationships with different stakeholder groups. This includes communication plans, involvement strategies, and conflict resolution approaches.
- Mitigate Risks: By understanding the potential risks associated with each stakeholder group, organizations can proactively address challenges, mitigate conflicts, and enhance the likelihood of project success.
Stakeholder analysis is a dynamic process that evolves throughout the lifecycle of a project or change initiative. As circumstances change, new stakeholders may emerge, and the priorities of existing stakeholders may shift. Therefore, continuous monitoring and adaptation of the stakeholder ecosystem map and engagement strategies are essential for effective change management.
Various methods and tools are employed to conduct stakeholder analysis. These can include a stakeholder analysis power interest matrix, a Miro stakeholder map, an Agile stakeholder map, onion model stakeholder analysis, OCMS Portal stakeholder analysis, or others.
These methods and tools help organizations visualize and categorize stakeholders, understand their dynamics, and create actionable plans for engagement and communication.
Ultimately, a well-executed stakeholder analysis contributes to building support, reducing resistance, and ensuring the successful implementation of organizational changes.
Do you have any questions about a stakeholder analysis NHS map, Mendelow matrix stakeholder mapping, stakeholder mapping power interest matrix, or stakeholder network map? Please reach out and let us know.
Why Should You Do a Stakeholder Analysis?
Stakeholder analysis is important because it helps you:
- Gain support and buy-in from the key stakeholders who can facilitate or hinder the change
- Avoid or minimize conflicts and resistance from the stakeholders who are negatively affected by the change
- Align the change objectives and benefits with the stakeholder interests and values
- Increase the stakeholder engagement and participation in the change process
- Enhance the stakeholder trust and credibility in the change management team
OCMS Portal’s Free Stakeholder Tools and Stakeholder Network Map

Want to streamline your change management activities? OCMS Portal has free templates you can use to plan and execute effective stakeholder engagement. Plus! When you sign up for a free trial, you gain access to all our change management tools including one you can use for stakeholder mapping interest and influence. Sign up below (no card needed).
What Tools & Models Help with Stakeholder Assessment?
How you handle your assessments – power influence grid stakeholder analysis, Mendelows stakeholder mapping, stakeholder heat map, etc. – will depend upon things like the change management framework and theories that are governing your project.
There are various tools and methods that you can use to conduct a stakeholder analysis, depending on the scope, complexity and nature of the change project. Here are some of the most common ones that we’ll be covering in more detail below:
- Mendelow stakeholder analysis
- Power interest grid stakeholder analysis
- Stakeholder heat map
- Stakeholder relationship map
- Stakeholder ecosystem map
- Agile stakeholder map
- Onion stakeholder map
- Johnson and Scholes stakeholder mapping
- Stakeholder mapping interest and influence
- Bateson stakeholder map
- Eden and Ackermann stakeholder mapping
- Stakeholder mapping cube
- OCMS Portal’s Stakeholder Assessment Tool
- Miro stakeholder map
- Smaply stakeholder map
- Mindtools stakeholder analysis
- Mural stakeholder map
- Luma stakeholder mapping
- Kumu stakeholder map
- Smartsheet stakeholder analysis
- Confluence stakeholder map
Do you have any questions NHS improvement stakeholder analysis, Mind Tools stakeholder analysis, stakeholder mapping Miro templates, or a power grid stakeholder analysis? Please reach out and let us know.
Stakeholder Analysis Methods & Models
As we know, in the realm of organizational change and project management, understanding and effectively engaging with stakeholders is paramount to success. A myriad of stakeholder assessment methods and models have been developed to provide a structured approach to identify, analyze, and manage stakeholders throughout the lifecycle of an initiative.
These frameworks offer diverse perspectives, ranging from power and interest dynamics to cultural and ethical considerations. In this comprehensive listing, we will explore various stakeholder assessment methods and models, each with its unique approach, insights, and applications.
From classic models like Mendelow’s Stakeholder Mapping to innovative stakeholder power maps, this compilation aims to serve as a guide for practitioners seeking to navigate the intricate landscape of stakeholder analysis, ultimately enhancing the strategic planning and execution of organizational endeavors.
Mendelow’s Stakeholder Mapping
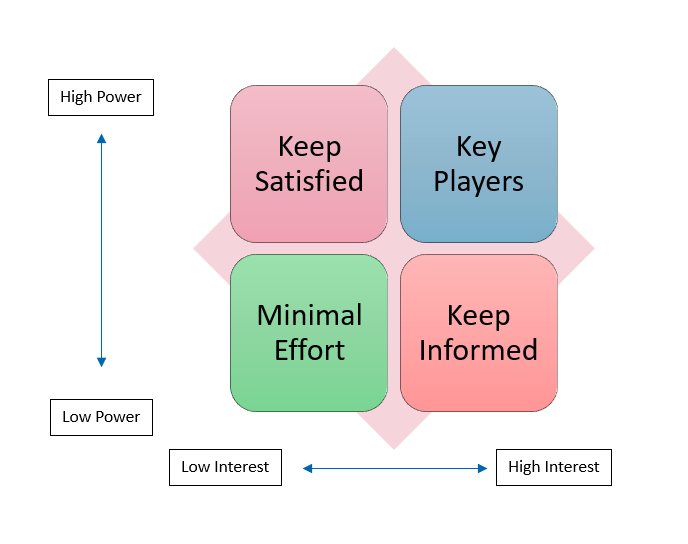
The stakeholder analysis Mendelow matrix categorizes stakeholders based on their level of power and interest in a particular change. Stakeholders are classified into four groups:
- Key Players (high power, high interest)
- Keep Satisfied (high power, low interest)
- Keep Informed (low power, high interest)
- Minimal Effort (low power, low interest)
This method aids in tailoring communication and engagement strategies for each group.
Power Interest Grid Stakeholder Analysis
The power matrix stakeholder analysis method plots stakeholders on a grid based on their power and interest, similar to Mendelow’s approach. The grid allows for a visual representation of stakeholder dynamics, helping prioritize efforts to manage and engage with them effectively. It may use slightly different descriptors than the ones in the Mendelow 1991 stakeholder mapping, such as “low priority” instead of “minimal effort.”
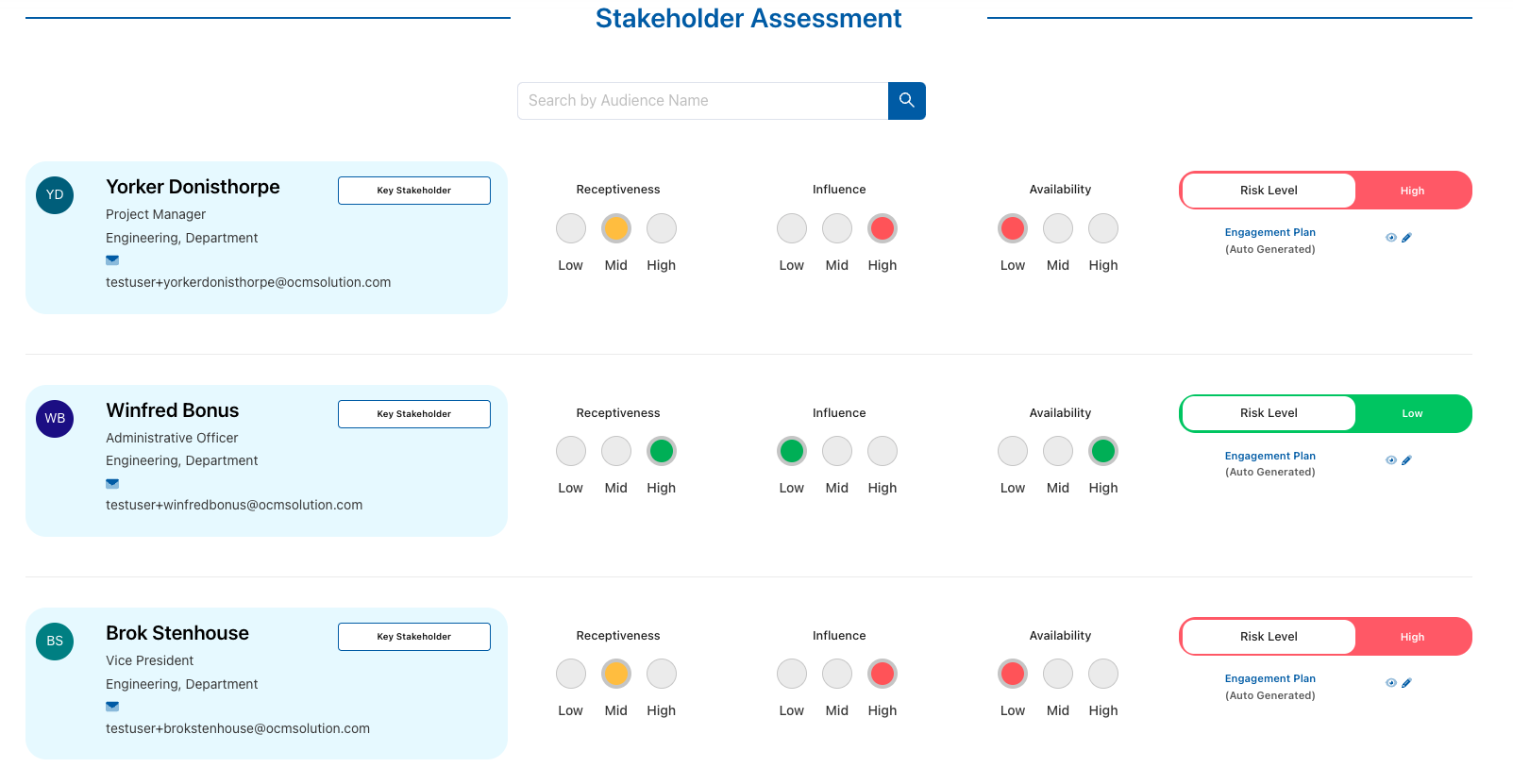
Stakeholder Heat Map
A stakeholder heat map visually represents the intensity of interest and influence of various stakeholders. This method is valuable for quick assessments, allowing change managers to focus on high-impact stakeholders and allocate resources accordingly.
One example of a Stakeholder Heat Map – from the OCMS Portal’s Stakeholder Tool
This stakeholder interest map in the OCMS Portal’s Stakeholder Assessment Tool uses colors for “high, mid, and low” and automatically generates a Risk Level for each stakeholder, making it easy to prioritize stakeholder engagement.
Stakeholder Relationship Map
This method emphasizes the connections and relationships among stakeholders. By mapping these relationships, change managers can identify potential alliances, conflicts, or dependencies that might impact the change initiative.
Stakeholder Ecosystem Map
The stakeholder ecosystem map takes a holistic approach by considering the broader organizational environment. It helps in understanding the interconnectedness of stakeholders and their relationships with external factors.
Agile Stakeholder Map
Tailored for Agile methodologies, this method emphasizes collaboration and adaptability. It involves continuous feedback and engagement with stakeholders throughout the change process, aligning well with the iterative nature of Agile projects. An Agile Stakeholder Map may change per each sprint in the project, for example, one group may be impacted in Sprint 1, and different groups maybe impacted during Sprint 2.
Onion Model Stakeholder Analysis
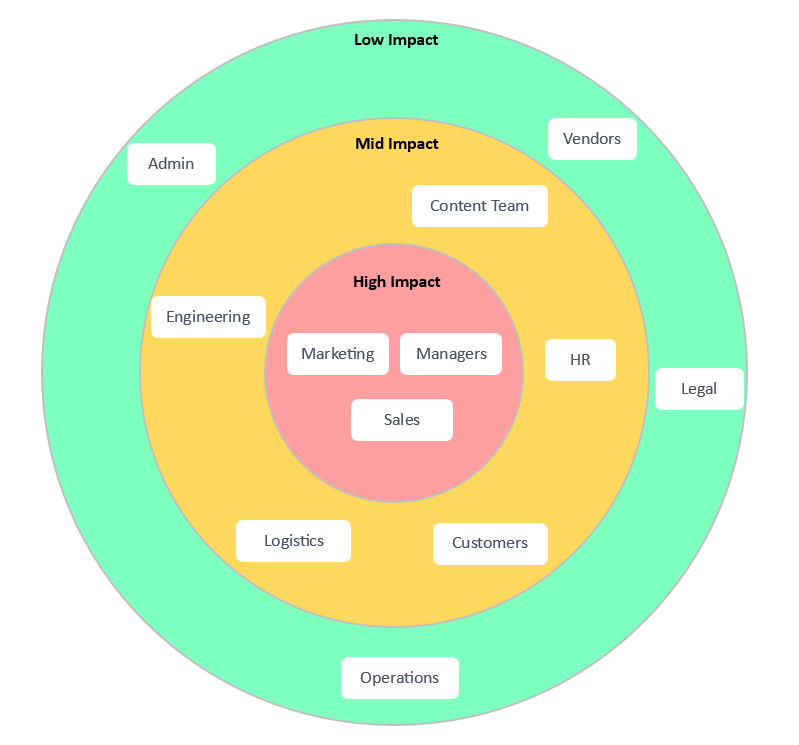
The onion stakeholder map views stakeholders in layers, with the core representing those directly affected by the change and outer layers representing indirect stakeholders. This method aids in understanding the ripple effects of change throughout the organization. When creating an onion model stakeholder analysis, you can use levels of impact for the layers of the onion, or something like direct, and indirect.
Johnson and Scholes Stakeholder Mapping: The Johnson and Scholes stakeholder mapping matrix is actually from Johnson, Scholes, and Wittingham. This is very similar to the stakeholder analysis power interest matrix in Mendelow’s example.
Bateson Stakeholder Map: The approach of the Bateson Stakeholder Map considers the level of emotional engagement of stakeholders. It categorizes then into six groups: critics, cynics, spectators, unengaged, ambassadors, and enthusiast.
Eden and Ackermann Stakeholder Mapping: This method is another example that is very close to the Mendelow matrix stakeholder analysis. It uses a similar power map stakeholder analysis, looking at four categories correlating to interest level and influence or power level.
Stakeholder Mapping Cube: The stakeholder mapping cube is a three-dimensional model that considers the two dimensions of power/influence and interest, like the Mendelow matrix stakeholder mapping and other stakeholder mapping power interest matrix models. But the Stakeholder Mapping Cube adds a third element – the person’s attitude or level of receptiveness to the change initiative. This method allows for a nuanced analysis by capturing the complexity of stakeholder relationships.
Do you have any questions about the Eden and Ackermann 1998 stakeholder analysis, a stakeholder map circle, stakeholder interest map, or stakeholder value network map? Please reach out and let us know.
Tools to Help with a Stakeholder Analysis
To facilitate this essential aspect of project management, a myriad of tools have been developed to streamline the identification, assessment, and engagement of stakeholders. Here are a few of those that you can leverage.
Tools for Stakeholder Analysis:
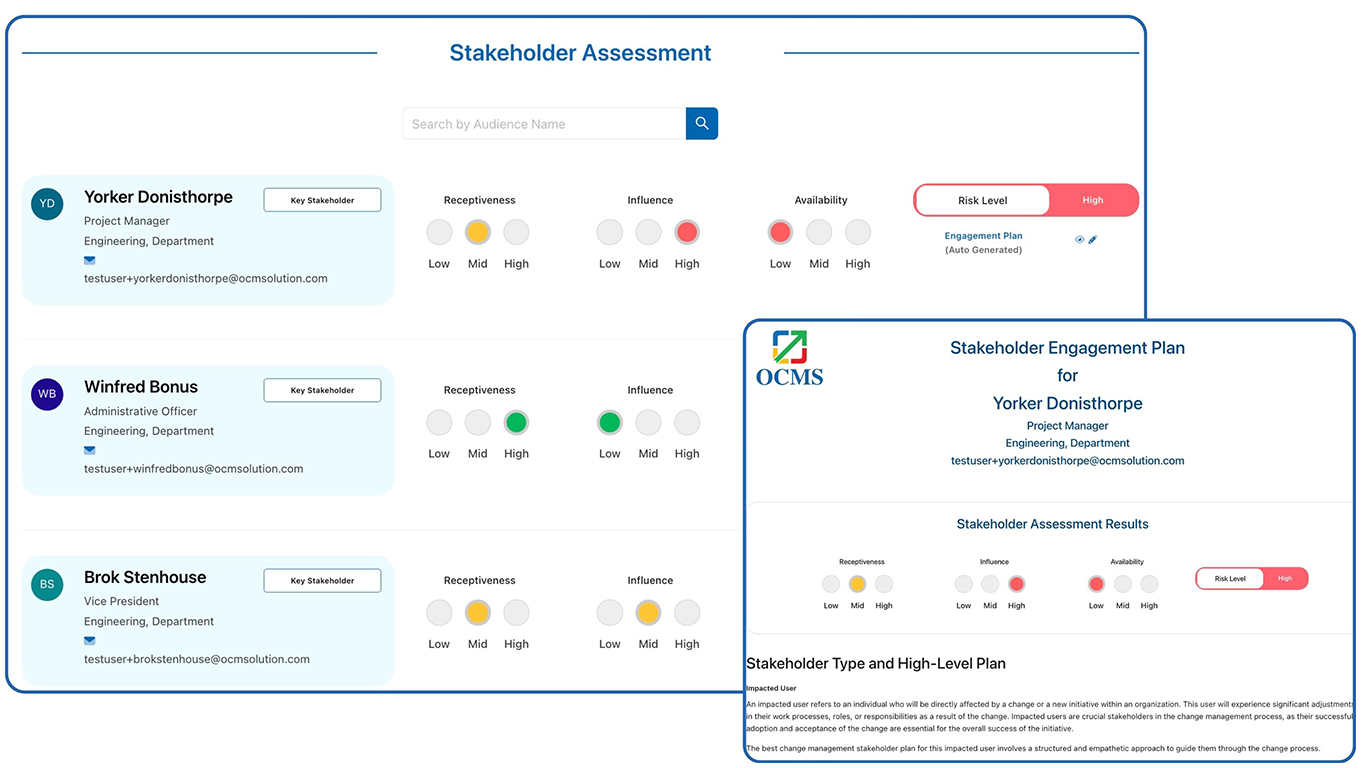
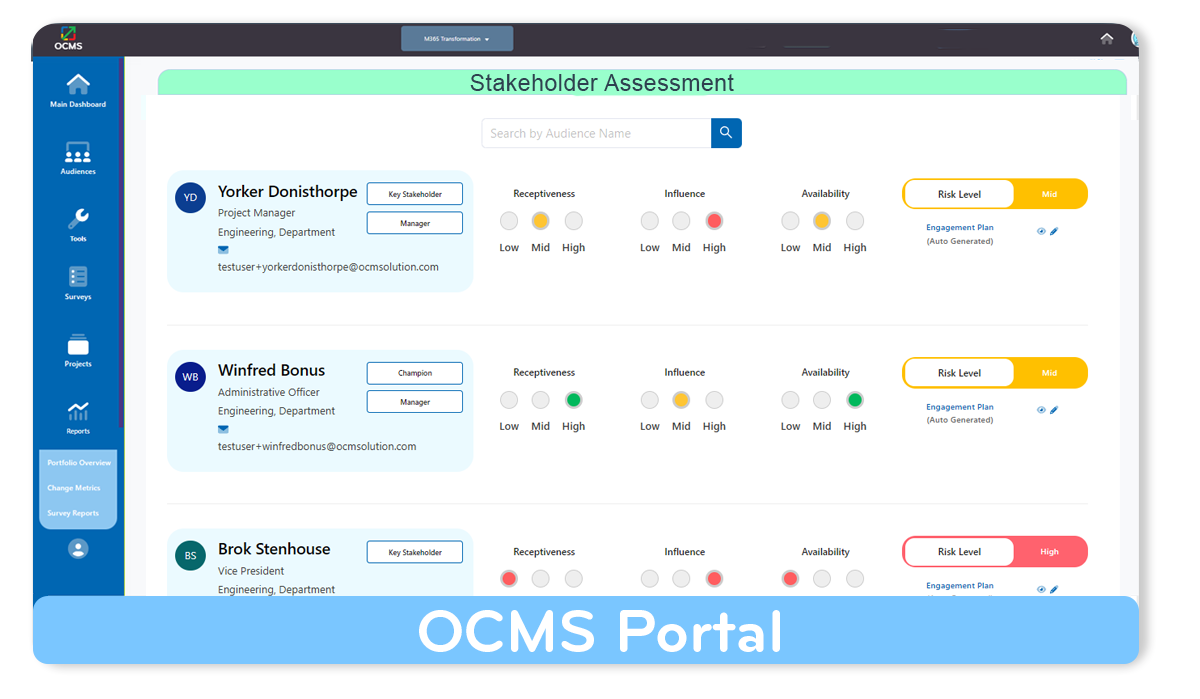
OCMS Portal’s Stakeholder Assessment Tool: This cloud-based tool is part of a full suite of change management tools that streamline the end-to-end process of change management. It incorporates a built-in stakeholder assessment survey and autogenerated stakeholder engagement plan based on the individual’s or group’s assessment. Learn more about this leading OCM software here.
Miro Stakeholder Map: Miro stakeholder map is an online collaborative platform that enables teams to create visual stakeholder maps. Its real-time collaboration features make it a popular choice for distributed teams working on stakeholder analysis.
Smaply Stakeholder Map: Smaply is a tool that includes features for creating stakeholder maps. It is particularly useful for organizations that looking for something like a stakeholder value map.
MindTools Stakeholder Analysis: MindTools offers an online platform with resources and templates for stakeholder analysis. Their tools guide users through the process of identifying and prioritizing stakeholders based on power, interest, and influence.
Mural Stakeholder Map: Mural is a digital workspace that facilitates collaborative stakeholder mapping. It provides a canvas for teams to visualize and organize stakeholders into a stakeholder mapping power interest matrix.
Luma Stakeholder Mapping: Luma is a learning platform that includes methods for stakeholder mapping. It combines visual thinking and collaboration techniques to enhance the ideation and analysis phases of stakeholder engagement.
Kumu Stakeholder Map: Kumu is an online stakeholder map creator where you can use a tree-like structure to visualize stakeholder relationships and create a stakeholder ecosystem map.
Smartsheet Stakeholder Analysis: Smartsheet is a well-known project management and collaboration tool that offers templates for stakeholder analysis. It allows teams to create dynamic sheets for tracking and managing stakeholder information.
Confluence Stakeholder Map: Confluence, a collaboration platform by Atlassian, provides tools for creating and sharing stakeholder maps. It integrates seamlessly with other project management tools, making it convenient for organizations already using the Atlassian ecosystem
OCMS Portal’s Stakeholder Analysis Mapping Tool (with Surveys & Autogenerated Engagement Plans)
If you need a great, streamlined tool to conduct a stakeholder analysis, you can try OCMS Portal’s stakeholder tool for free now. Just sign up for a free trial below (no card needed).
Conclusion: Stakeholder Mapping Meaning
In wrapping up our exploration of stakeholder analysis and mapping, it’s clear that understanding your project’s influencers is the key to unlocking its full potential. By delving into the unique needs of stakeholders, you’re not just ensuring their support; you’re building a community of cheerleaders for your project.
Remember, key stakeholder analysis isn’t a one-time task but an ongoing conversation. Continuously reassess, communicate, and adapt your strategies as your project evolves. Embrace the insights gained here, and watch how your projects transform from mere tasks into collaborative achievements, making a real impact on your organization and beyond.
OCMS Portal is a full-featured cloud platform to help you plan, manage, and execute a successful change project, end-to-end, whether this is your first change project or your one-hundredth. You can choose from multiple change tools, including the Stakeholder Analysis Tool.
FAQ: Stakeholder Analysis Tools & Methods
Stakeholder analysis is the process of assessing the stakeholders for a project or change. Stakeholder analysis is a critical component of effective project and change management because it increases the success of your stakeholder engagement and management. Read more in this article
There are several methods you can choose from when doing an analysis of stakeholders for a change initiative. Some of these are: Mendelows Stakeholder Mapping, Stakeholder Relationship Map, Stakeholder Heat Map, Power Grid Stakeholder Analysis, Onion Model Stakeholder Analysis, among others.
A stakeholder analysis is important because it allows you to document and determine each stakeholder’s level of commitment to the change (negative or positive), so you can effectively plan on how best to enlist their buy-in and support, or how to mitigate their resistance.
Popular tools to use to create a stakeholder analysis include: OCMS Portal's Stakeholder Assessment Tool, stakeholder map Miro, Smaply Stakeholder Map, Mind Tools Stakeholder Map, Mural Stakeholder Map, Luma Stakeholder Mapping, and others.What is Stakeholder Analysis?
What are some methods used for stakeholder analysis?
Why is a stakeholder analysis important?
What are some tools people use as a stakeholder map creator?
Note: Content on OCM Solution's ocmsolution.com website is protected by copyright. Should you have any questions or comments regarding this OCM Solutions page, please reach out to Ogbe Airiodion (Change Management Lead) or the OCM Solutions Team today. OCM Solution was previously known as Airiodion Global Services (AGS).
External source: Stock.adobe.com,